Eating too much sugar can give you diabetes! Myth or Fact?
Not necessarily! Diabetes develops due to a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. When it comes to Type 2 Diabetes, physical inactivity and being overweight are the two main culprits. Your body weight increases when you consume more calories than what you burn, and this is not dependent on the amount of sugar you have.
To manage the condition well, it is important that you are aware of the facts on diabetes as it can have serious effects on your health.
What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic lifestyle disease where your blood sugar levels are high. In Type 2 Diabetes there are two interrelated problems. First, your cells develop resistance to insulin (a hormone that regulates the amount of glucose in your bloodstream), and second, your pancreas fails to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand.
Type 2 Diabetes is more common in older adults. However, the changes in lifestyle and the increase in childhood obesity have led to more cases of Type 2 Diabetes in younger individuals.
What Causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Your pancreas produces a hormone called insulin that converts glucose, a type of sugar from the food you eat, into energy. Insulin circulates in your bloodstream and facilitates the entry of glucose into your cells where it will be converted. Therefore, it helps regulate the sugar levels in your bloodstream.
In certain situations where your blood glucose drops, in response to it, your pancreas produces less insulin.
In Type 2 Diabetes, this process doesn’t work in the normal way. Instead of entering into your cells, glucose or sugar builds up in your system. This leads to an increased glucose level in your blood. In response to this increase, your pancreas releases more insulin, and at one point in time the cells get impaired, and they become unable to keep up with the demand.
What are the Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes?
Multiple factors increase the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes:
Body Weight:
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes.
Activity Levels:
Leading a sedentary lifestyle is one of the risk factors for Type 2 Diabetes. Regular exercise helps you maintain a healthy weight and prevent obesity.
Family History:
Having a family member with diabetes increases your chances of developing the condition.
Lipid Levels:
An increase in the bad cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein – LDL) levels in your body and a drop in the good cholesterol (High-density lipoprotein – HDL) levels can put you at risk of Type 2 Diabetes.
PCOS:
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder in women that causes irregular menstrual cycles and fertility issues. PCOS increases the risk of diabetes.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes?
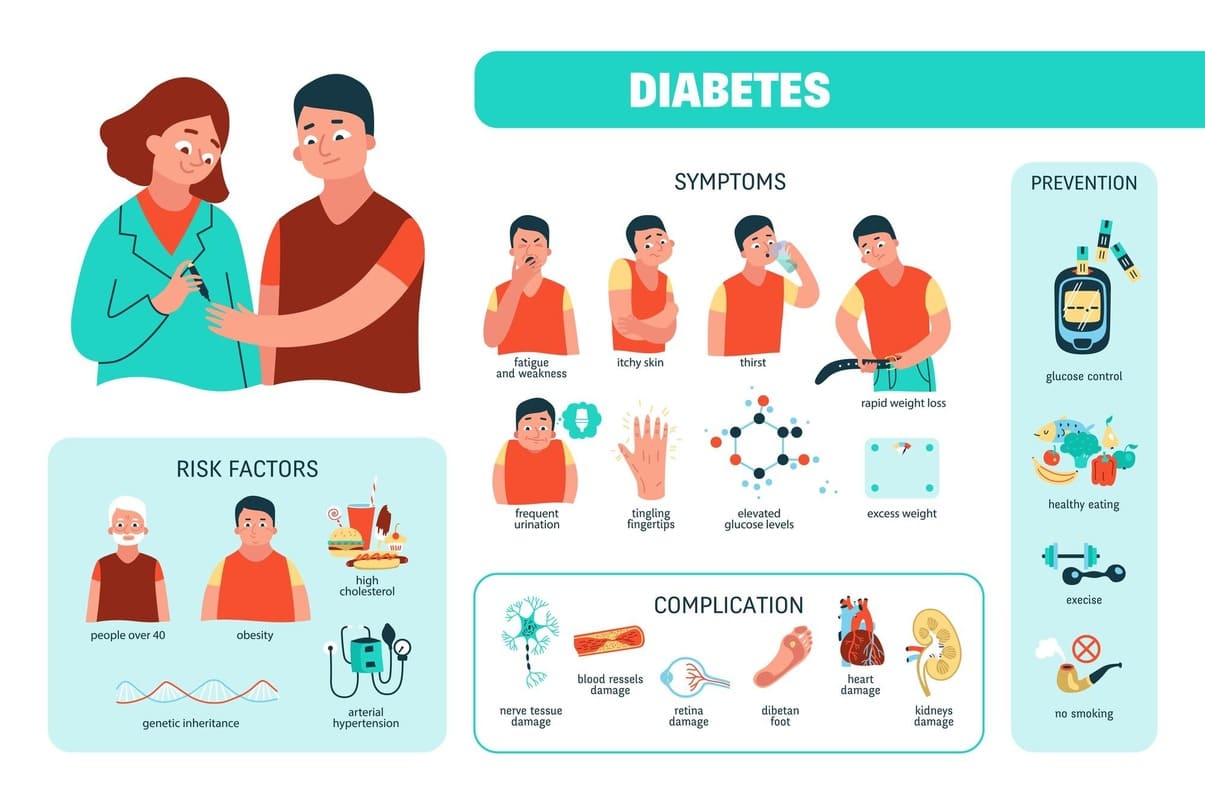
In Type 2 Diabetes your body is unable to effectively convert glucose into energy. This causes your body to rely on alternative energy sources leading to a variety of symptoms. Some of the early signs include:
- Fatigue
- Constant hunger (polyphagia)
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Unintended weight loss
- Changes in vision
- Frequent infections
- Slow healing sores
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet
- Area of darkened skin
How is Type 2 Diabetes Diagnosed?
If you think you are experiencing symptoms of diabetes, make sure that you visit your doctor without any further delay. Your doctor will perform the following tests to determine if you have diabetes.
Hemoglobin A1C Test:
This test helps determine your average blood glucose levels for the past 2 to 3 months. A blood glucose level of 5.7% or below is considered normal, and a level of 6.5 % or higher is considered a sign of diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Test:
This test is done at any time regardless of when you had your last meal. A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL indicates that you have diabetes.
Fasting Blood Sugar Test:
This test measures your blood sugar levels after overnight fasting. A level of 99 mg/dL is normal and 126 mg/dL or higher indicates that you have diabetes.
Glucose Tolerance Test:
This test measures your blood glucose levels before and after you have a glucose drink. This drink has to be taken after you fast overnight. Your blood sugar levels will be checked at periodic intervals (in 1 hour, 2, and 3 hours). A blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates that you have diabetes.
If you are at risk of developing diabetes, it is better to undergo routine screenings once a year to detect any changes in your blood sugar levels at an early stage. This will help in managing the condition better.
Discover everything about diabetes, including its types, genetic connections, and related conditions such as heart disease, thyroid, and blood pressure concerns
Know the Management of Type 2 Diabetes
You can manage Type 2 Diabetes with the following measures:
Healthy Diet
There is no specific diabetic diet that you need to follow. However, making small dietary changes can help you manage Type 2 Diabetes. You can include more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and low-fat dairy in your meals. Also, try to have smaller portions multiple times a day.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is necessary to control your blood sugar levels. If you are overweight, even a minor change in your body weight can lead to a considerable change in your blood sugar levels. Having a healthy diet plan and staying active can help you manage your weight.
Regular Exercise
Make sure to stay active and exercise regularly. Other than maintaining a healthy weight it also helps you control your blood sugar levels. Aim for 30 minutes of exercise for at least 5 days a week. You can include aerobic exercises such as running or biking and low-impact exercises such as yoga or pilates in your workout plan.
Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly can help you detect any changes in your blood sugar and take action early. This can be helpful, especially if you are at risk of developing diabetes.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
Make sure that you take your medications regularly as prescribed by your doctor. Some may require insulin therapy if medications are not giving the desired results.
What are the Complications of Type 2 Diabetes?
The following are some of the major complications caused by uncontrolled and untreated Type 2 Diabetes:
Heart Disease
Long-standing diabetes can damage the blood vessels that supply your heart affecting its function. Diabetes can increase the risk of cardiovascular conditions such as heart attack, stroke, or atherosclerosis (plaque build-up in the blood vessels).
Nerve Damage
Diabetes can lead to nerve damage which leads to loss of sensation, tingling, and numbness in your extremities. It can also cause digestive issues such as nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
Kidney Damage
Diabetes can cause damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys. It affects the normal functioning of your kidneys and increases the chances of kidney damage and also puts you at risk of developing high blood pressure.
Vision Problems
Chronic diabetes can damage the blood vessels in your eye causing changes in vision and in some cases even blindness. It also increases your chances of developing eye diseases such as cataracts and glaucoma.
Infections
Diabetes increases your chances of developing bacterial and fungal infections that can weaken your immune system, making you prone to infections.
Hearing Impairment
Diabetes can eventually affect the blood vessels in your ear causing problems with hearing. In some cases, it can lead to complete hearing loss.
Sleep Problems
Diabetes can cause sleep problems such as obstructive sleep apnea. It involves brief periods of pauses in breathing during your sleep. This can lead to a drop in the oxygen levels in your blood causing damage to your vital organs.
Dementia
Dementia is a condition that affects your cognitive function. Diabetes can lead to the damage of blood vessels in the brain which may contribute to cognitive decline.
Is it Possible to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?
It is possible to prevent Type 2 Diabetes even if you are someone with a family history of diabetes. By adopting a healthy lifestyle you can reduce the risk of developing diabetes. This includes measures such as eating healthy, staying active, maintaining an ideal weight, and getting regular health check-ups.
Don’t Have Time To Read?
- Type 2 Diabetes is a chronic lifestyle disease where your blood sugar levels are high. Here your cells are unable to use insulin effectively.
- In Type 2 Diabetes, instead of entering into your cells, glucose builds up in your system. This leads to increased glucose levels in your blood. In response to this increase, your pancreas releases more insulin and at one point in time, the cells get impaired because of unmet demand.
- An inactive lifestyle and obesity are the major risk factors for the development of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Fatigue, constant hunger, increased thirst, and unintentional weight loss are the common symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Type 2 Diabetes can be effectively managed through a healthy diet, regular exercise, maintaining a healthy body weight, and proper medications.
- By adopting a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
Friendly Asked Questions
What is the difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune condition where your body mistakenly attacks the cells of your pancreas that produce insulin. It mostly affects children and young adults. Type 2 Diabetes occurs when your body is not able to use insulin effectively. It mostly affects older adults.
Which is worse, Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes?
Both Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes can cause significant health complications. Therefore one cannot be termed as worse than the other.
Can Type 2 Diabetes be reversed?
Type 2 Diabetes cannot be reversed. However, with healthy lifestyle modifications and proper medications, the condition can be managed well.
What is a good diet for a diabetic?
It is important that diabetics choose a healthy diet as diet plays a major role in managing diabetes. You can try to include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy, nuts and seeds in your daily diet. You can avoid starchy food such as potatoes, rice, bread, and pasta.Including it among your many other diabetes management practices can help a little. And there’s no doubt that it could benefit your health in ways other than blood sugar control.
Can Type 2 Diabetes affect children?
Type 2 Diabetes commonly affects older adults. However, due to the changes in our lifestyle and the increase in childhood obesity, nowadays, Type 2 Diabetes is also seen in children and young adults.
Can I live a normal life with Type 2 Diabetes?
Yes! You can live a normal life with Type 2 diabetes. With a healthy lifestyle, proper medications, and regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels you can lead a normal life with diabetes.
Does Type 2 Diabetes get worse with age?
Type 2 Diabetes is a progressive condition, and it worsens with time unless you manage it well. Advancing age is a risk factor for Type 2 Diabetes.
